Pathology is a branch of medical science primary this is diagnosis branch . It involves the examination of Blood , organs, body fluids, and autopsies in order to study and diagnose disease.
Currently, pathology can be divided into eight main sections , depending on the types of methods used or the types of diseases examined. These different disciplines are described below.
1)Hematology
2)Clinical pathology
3)Biochemistry
4)Immunology
5)Microbiology &Infectious Serology
6) Cytology
7)Histopatholoy
8)Molecular biology
* Hematology : Hematology is the section for that involves the study of the blood cell and mechanisms behind cell and tissue injury and understanding how the body responds to and repairs injury. Examples of areas that may be studied include necrosis, neoplasia, wound healing, inflammation and how cells adapt to injury.
This field is concerned with various different disease aspects that affect the blood, including bleeding disorders, clotting problems, and anemia, for example. Another area of hematology is transfusion medicine, which involves performing blood typing, cross-matching for compatibility and managing large amounts of blood products. An example of a test a hematologist may perform is a blood clotting test to check whether a patient’s dose of warfarin needs increasing or decreasing.
*Clinical Pathology : Laboratory medicine, clinical pathology concerns the commonly analysis of urine, Stool and Body fluids samples to examine and diagnose disease. Examples of the information clinical pathology laboratories may provide include cell count, microscope results.
(Microscope Examination of Urine )
*Biochemistry : Biochemistry section examine all aspects of disease, identifying changes in various different substances found in the blood and bodily fluids such as proteins, hormones and electrolytes since these changes can indicate and provide clues about disease or disease risk.
For example, a biochemist may assess cholesterol and triglyceride levels in order to determine heart disease risk. They may also look for and measure tumor markers, vitamins, poisons, medication. depending on blood suger levels diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. recently laborotarys used fully autometed Biochemistry equipments for diagnosis.
*Immunology /Immunoassay: Immunology section perform immune function tests to establish whether or not a patient is suffering from an allergy and if so, what they are allergic to. Many diseases also arise as a result of the immune system having an abnormal reaction to healthy cells or tissues and launching an immune attack against them. This is referred to as a autoimmune disease. There is a range of immunological tests that can detect markers of autoimmune diseases. diagnosis of Vitamin deficency ,Serum IgE for Allergy .
*Microbiology & Infectious serology:
(Microbiology Sample processing area)
Microbiology section is concerned with diseases caused by pathogenic agents such as bacteria, viruses, parasites and fungi. Samples of blood, bodily fluid and tissue are tested and diagnosis whether infection exists or not , and the field of medical microbiology is also engaged with identifying new species of microorganisms.One of the principal roles of the microbiologist is to make sure that antimicrobial drugs are prescribed and used appropriately.deu to Antibiotic sensitivity trsting in Microbiology section.
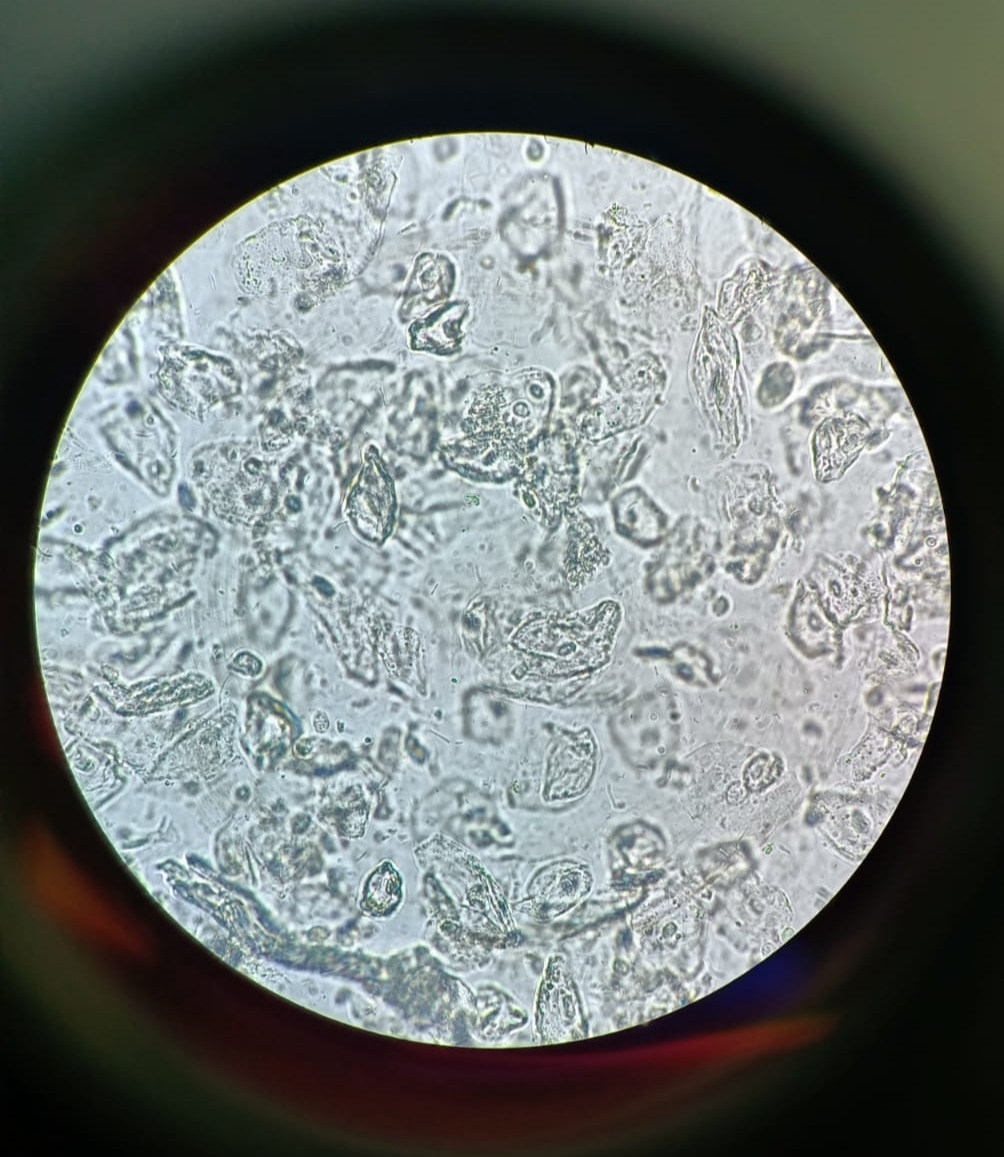
*Cytology : Cytology is the study of the cellls especially their appearance and structure. Cells are the small parts that make up all living things, and their effects on each other and their enviornment.
There are two types of cells. procariotic cells do not have a clear and easy-to-see nucleous and do not have a membrane or wall, around them. eukariotic cells have an easy-to-see nucleus where all of the cell's functions take place, and a membrane around them. The main orgenless of a cell and their uses are:
- Mitochondia: produces energy for the cell
- Endoplasmic recticulom makes proteins and carbohydrats for the cell to use
- Golgi bodies: store and package products that the cell uses
- Plastid (present in plant cells only): contains chemicals needed photosynthesis in plants only.
- Nucleous: directs the actions of the cell
- Centerosoms: guides the cell in mitosis and meiosis, the processes for cell division
- The pre-analytical phase, which involves obtaining patient information and taking the specimen sample.
- The analytical phase, which involves examining and testing the sample.
- The post-analytical phase, which involves analyzing the test results and creating an official report.













1 Comments
Thank you Pradeep Sir for sharing such a knowledgeable information regarding Pathology. Waiting for your next blog
ReplyDelete